Hoff’s syndrome, also known as lipoma arborescens, is a common condition that affects the fatty tissue around the knee joint, especially at the bottom.
This condition is characterized by an abnormal increase in fatty tissue in the joint, which can cause pain, inflammation and limited movement. In this article, we will take a closer look at diagnostic methods and treatment options for Hoffa syndrome. Everyone can find out more information on the website https://eldolorderodilla.com.
Clinical history and physical examination
Initially, the doctor takes a detailed medical history, finding out the patient’s symptoms and medical history. A physical examination of the knee joint is then performed to evaluate its condition, identifying pain points, swelling, and limited range of motion. The doctor may ask the patient to perform various movements to determine which ones cause pain.
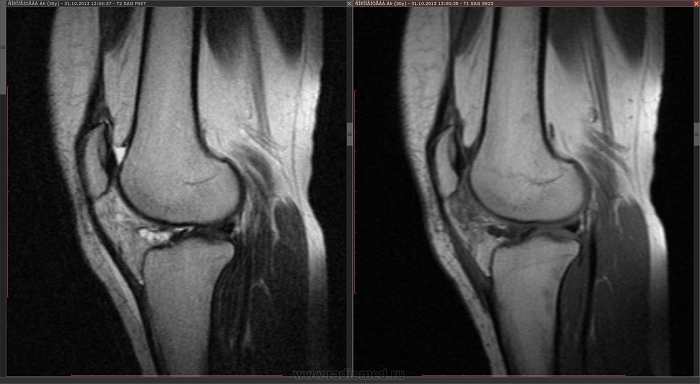
Imaging studies
Various imaging techniques are used to accurately diagnose and rule out other possible causes of symptoms:
- radiography;
- Ultrasound;
- MRI.
In some cases, joint aspiration may be necessary, a procedure in which synovial fluid is removed from the joint for analysis. This helps rule out infection or other conditions such as gout or rheumatoid arthritis.
Treatment of Hoff’s syndrome
Treatment for Hoffa syndrome can be conservative or surgical, depending on the severity of symptoms and response to initial therapy. Your doctor may prescribe medication or physical therapy. Physiotherapy prescribes special exercises and procedures aimed at strengthening the muscles around the knee joint, improving its mobility and reducing the load on the affected fatty tissue. Sometimes injection or surgical treatment is also prescribed.










Leave a Reply
View Comments